Место работы автора, адрес/электронная почта: ФИЦ "Якутский научный центр СО РАН", Институт космофизических исследований и аэрономии им. Ю.Г. Шафера СО РАН ; 677980, г. Якутск, пр. Ленина 31 ; e-mail: s_samsonov@ikfia.ysn.ru ; https://ikfia.ysn.ru/institute/
Ученая степень, ученое звание: канд. физ.-мат. наук
ID Автора: РИНЦ AuthorID: 58577
Деятельность: В 1974-1995 гг. работал научным сотрудником, заведующим лабораторией жестких излучений (1993-1995), с 1999 г. - старший научный сотрудник лаборатории магнитосферных частиц в Институте космофизических исследований и аэрономии им. Ю.Г. Шафера.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Manifestation of Magnetosphere Fluctuations during the Large Magnetic Storm of January 21-22, 2005 / D. G. Baishev, E. S. Barkova, V. A. Mullayarov, S. N. Samsonov, S. I. Solovyev, K. Yumoto // Solar Extreme Events Fundamental Science and Applied Aspects Nor-Amberd, Armenia 26-30 September 2005 : proceedings of the Second International Symposium / edited by A. Chilingarian and G. Karapetyan. − Erevan : Cosmic Ray Division, Alikhanyan Physics Institute, 2006. − P. 96-99.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
Skryabin, N. G. Influence of a change in solar magnetic field polarity on the Jovian electron flux intensity / N. G. Skryabin, S. N. Samsonov, I. Ya. Plotnikov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 159-161.
Количество страниц: 3 с.
Sokolov, V. D. The dynamics of auroral absorption parameters in the 22nd solar activity cycle / V. D. Sokolov, S. N. Samsonov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 95-97.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
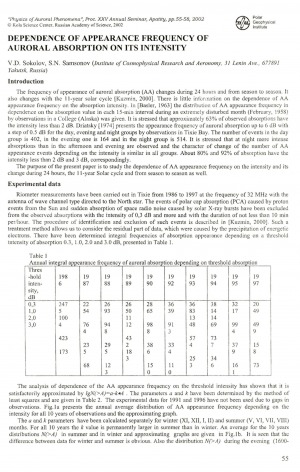
Sokolov, V. D. Dependence of semi-diurnal variation of auroral absorption on a geomagnetic disturbance / V. D. Sokolov, A. A. Danilov, S. N. Samsonov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 26th annual seminar, 25 - 28 February 2003. – 2003. – P. 91-94.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Skryabin, N. G. Influence of Jupiter on cosmic ray intensity variations / N. G. Skryabin, S. N. Samsonov, I. Ya. Plotnikov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 25th annual seminar, Apatity, 26 February – 1 March 2002. – 2002. – P. 137-139.
Количество страниц: 4 с.
Sokolov, V. D. Dependence of appearance frequency of auroral absorption on its intensity / V. D. Sokolov, S. N. Samsonov // Physics of auroral phenomena : proceedings of the 25th annual seminar, Apatity, 26 February – 1 March 2002. – 2002. – P. 55-58.
Количество страниц: 9 с.
- Математика. Естественные науки > Астрономия. Астрофизика. Исследование космического пространства. Геодезия,
- Математика. Естественные науки > Геология. Геологические и геофизические науки,
- НАУКА ЯКУТИИ > МАТЕМАТИКА. ЕСТЕСТВЕННЫЕ НАУКИ > Астрономия. Астрофизика. Исследование космического пространства. Геодезия,
- НАУКА ЯКУТИИ > МАТЕМАТИКА. ЕСТЕСТВЕННЫЕ НАУКИ > Геология. Геологические и геофизические науки.
Monitoring and investigating space weather effects with meridional chain of instruments in Yakutia: a brief overview = Мониторинг и исследование эффектов космической погоды с помощью меридиональной цепочки инструментов в Якутии: краткий обзор / D. G. Baihsev, S. N. Samsonov, A. V. Moiseev, R. N. Boroyev, A. E. Stepanov, V. I. Kozlov, A. A. Korsakov, A. A. Toropov, A. Yoshikawa, K. Yumoto // Солнечно-земная физика = Solar-Terrestrial Physics. – 2017, т. 3, N 2 : 13-я российско-китайская конференция по космической погоде. – С. 27-35.
DOI: 10.12737/22607